


Barnyard Millet
Barnyard Millets are valued for their high nutritional value and lower expense as compared to major cereals like rice, wheat, and maize. It contains a rich source of protein, carbohydrates, fiber, and, most notably, micronutrients like iron (Fe) and zine (Zn) that are related to numerous health benefits. These features make barnyard millet an ideal supplementary crop for subsistence farmers and also as an alternate crop during the failure of monsoons in rice/major crop cultivation areas.
Characteristics of Barnyard Millet
- Appearance: The grains are small and round, with a color that can range from white to pale yellow. They have a mild, nutty flavor.
- Growth: Barnyard millet is a hardy plant that can thrive in poor soil conditions and requires minimal water. It has a relatively short growing cycle, typically around 60-90 days.
- Harvest: The plant produces seed heads that are harvested when the grains are mature and dry.
Storage Instructions: Store in a clean and dry place - away from sunlight.
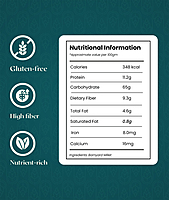
Nutritional Information
Approximate value per 100gm*
| Calories | 348 kcal |
| Protein | 11.2 g |
| Carbohydrates | 65 g |
| Dietary Fiber | 9.3 g |
| Total Fat | 4.6 g |
| Saturated Fat | 0.8 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 1.0 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 2.3 g |
| Iron | 8.0 mg |
| Calcium | 16 mg |
| Magnesium | 117 mg |
| Phosphorus | 266 mg |
| Potassium | 280 mg |
| Zinc | 1.9 mg |
| B Vitamins (Niacin) | 2.7 mg |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B1) | 0.3 mg |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 0.1 mg |
Culinary Uses
Breakfast Porridges: Cook Barnyard millet with water or milk to make a hearty and nutritious porridge. You can add fruits, nuts, seeds, and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup for extra flavor.
Salads: Cooked Barnyard millet can be used as a base for salads. Toss it with vegetables, herbs, and a light vinaigrette for a healthy and filling salad.
Side Dishes: Use Barnyard millet as a side dish similar to rice or couscous. It pairs well with vegetables, legumes, and protein sources like chicken, fish, or tofu.
Soups and Stews: Add Barnyard millet to soups and stews as a thickening agent and to enhance the nutritional value. It absorbs flavors well and adds a pleasant texture.
Pilafs: Prepare Barnyard millet pilaf by cooking it with spices, vegetables, and sometimes nuts or dried fruits. It can be a flavorful and nutritious alternative to traditional rice pilafs.
Baked Goods: Incorporate Barnyard millet flour into baked goods such as bread, muffins, and pancakes. It adds a unique texture and nutritional boost to these items.
Stuffings: Use cooked Barnyard millet as a stuffing for vegetables such as bell peppers, tomatoes, or zucchinis. Mix it with herbs, spices, and other ingredients for a flavorful filling.
Main Dishes: Create main dishes by combining Barnyard millet with legumes and vegetables to make hearty grain-based dishes like casseroles or grain bowls.
Energy Bars: Incorporate Barnyard millet into homemade energy bars or granola bars for added crunch and nutrition.
"Barnyard millet is a versatile and healthy grain that can be used in a variety of dishes, providing a nutritious alternative to other staple grains."
Ingredients: Barnyard Millet
